
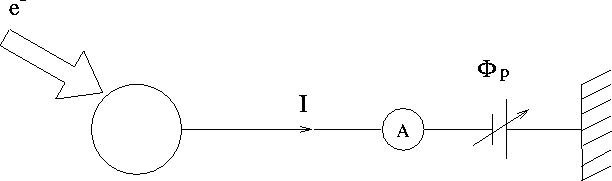
In density mesearement mode, the potential ![]() is fixed and the current I is measured. The plasma parameters can
be retrieved if a theoretical model of I is available. In principle,
a model of I must be determined by expressing each component of
the current using the distribution function at the surface of the object,
is fixed and the current I is measured. The plasma parameters can
be retrieved if a theoretical model of I is available. In principle,
a model of I must be determined by expressing each component of
the current using the distribution function at the surface of the object,
| (2) |
where
J is the current densities at the object surface. q is the charge of the particle. u is the speed of the particle. n is the normal to the surface. f is the distribution function.is the electric potential.
In general the determination of ![]() requires to solve the Vlasov-Poisson system of equation,
requires to solve the Vlasov-Poisson system of equation,
| (3) | |||
| (4) |
where
E is the electric field. B is the magnetic field. m is the mass of the particle.Fortunately, there are several possible simplifications of the problem leading to more tractable equations. For instance, it can be shown that in the case of a system with spherical symmetry and a radius much smaller than the plasma Debye-Length,
| (5) |
where
rp is the radius of the probe. ne is the electronic density. Te is the electronic temperature.is the potential of the probe.